In this article, we're going to look at the main types of athlete's foot.
All fungal infections are collectively referred to as mycoses. Experts divide them into two main categories - onychomycosis and dermatomycosis. In the first case, microorganisms penetrate under the nail, in the second the skin is affected. In addition, absolutely all types of athlete's foot are classified taking into account the pathogen and the main symptoms.
Main types
First of all, the type of fungus that affects the legs depends on the causative agent of the disease. Pathogenic microorganisms are divided into several groups: dermatophytes, yeasts and molds. They are able to provoke such common lesions as:
- Onychomycosis;
- Candidiasis;
- Epidermophytosis;
- Rubrophytic disease.
The latter is the general name for a group of pathologies that affect the feet. All diseases are also divided into groups according to clinical manifestations: membrane-like, moccasin-like, vesicular.
We'll look at the types of athlete's foot, photos, and treatment with alternative methods below.
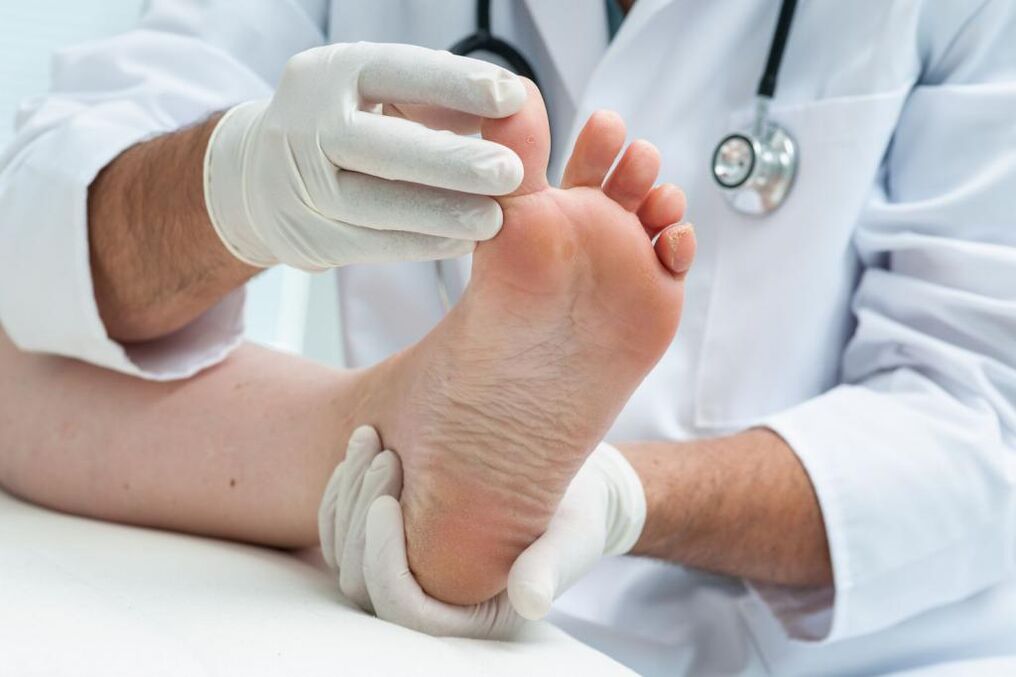
Rubrophytic disease
The second name of this disease is rubromycosis. It is characterized by overcrowding of blood vessels, dryness and severe flaking. The pathology develops very slowly and almost imperceptibly for a person who is sick with an infection.
Athlete's foot in the form of blisters is very uncomfortable.
The first signs are itching and flaking, which are already noticeable in later stages of the disease. Damage to the nails also occurs at this stage. Outwardly, the disease is manifested by the appearance of bubbles, crusts, plaques, pustules, localized over the entire surface of the sole. If a large number of plaques and blisters appear, then a person begins to experience painful sensations while walking.
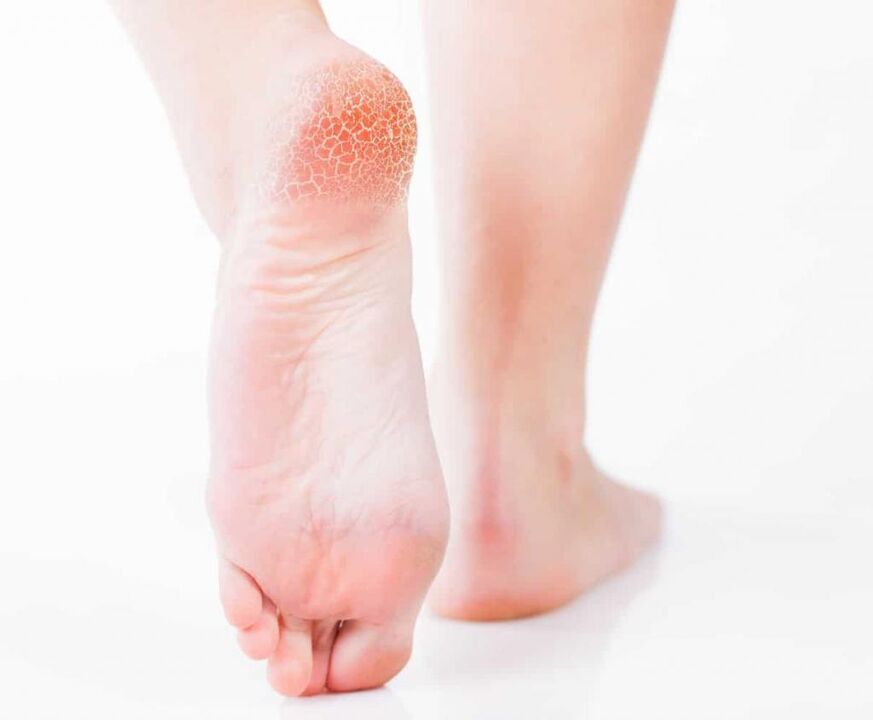
Determining the type of athlete's foot (pictured) plays a key role in treatment. Before prescribing therapy for rubrophytosis, it is necessary to conduct a microscopy and examine the clinical picture. Elimination of lesions is carried out using peeling (keratolytic) agents. Mostly these are ointments and creams based on salicylic acid. Therapy is usually complex. In parallel with external means, antifungal drugs are prescribed.
If the disease is severe, then you should start taking drugs in the form of pills. Lesions of the nail plates are treated by removing them with plasticizers.
This type of athlete's foot (see photo above) is characterized by a high level of infectivity. It is enough to touch the things that the carrier of the infection uses. The likelihood of infection increases many times over when a person suffers from excessive sweating, has a weakened immune system and the feet are damaged.
The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Tr. Mentagrophytesvar. It is able to penetrate the granular and stratum corneum layers of the skin, spread and cause severe allergic and other reactions:
- Pain when walking, burning and itching;
- Deformation and yellowing of the nails;
- the appearance of crusts, scales, painful cracks;
- Skin erosion (maceration);
- the appearance of pustules, edema;
- Vesicular rash with a dense crust.
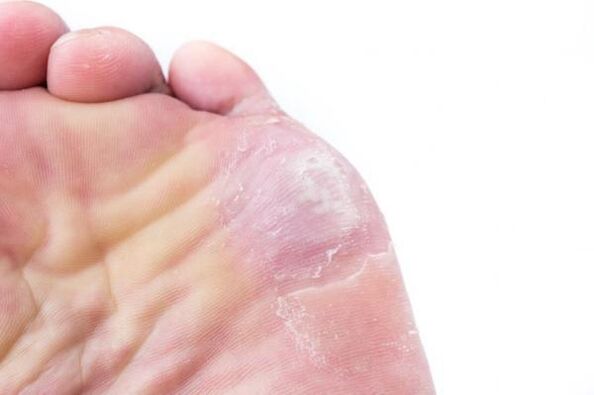
The diagnosis of this type of athlete's foot consists in the examination of its external signs and clinical picture. If the causative agent of the pathology is not obvious, a clinical examination may be necessary, for example, examining the scratching under a microscope.
The therapy of rubrophytosis in acute form includes the use of drugs based on silver nitrate 0, 25%, calcium 10% and meta-dihydroxybenzene 1%. If allergic reactions occur, antihistamines should be used. The choice of antifungal drug depends entirely on the clinical course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
What other types of athlete's foot are there?
Foot candidiasis
This type of fungus is much less common in patients than epidermophytosis or rubromycosis. The pathology occurs under the influence of a fungus belonging to the genus Candida. Such microorganisms live in the body of everyone, but are considered conditionally pathogenic. That is, in small quantities they pose no threat, but their rapid reproduction can cause unpleasant symptoms and consequences. The uncontrolled reproduction of the fungus begins when immunity decreases with hypothermia, overwork, or frequent stress. External factors are:
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes, especially in summer;
- injuries sustained at home or at work;
- constant maceration of the skin of the feet (skin peeling as a result of prolonged exposure to water).
There are two types of candidiasis of the feet: hyperkeratotic and more vesicular-pustular. The first form of candidiasis is characterized by a thickening of the stratum corneum. On it appear quite wide grooves of light brown color, which are constantly peeling off. For the purpose of diagnosis, a peeling is done and the particles in which candida fungi are found are examined further.

The viscous-pustular form of candidiasis manifests itself in the form of hyperemia (overcrowding of blood vessels), pronounced swelling, maceration. Areas of the affected skin are covered with pustules and small flat vesicles. After the inflammatory processes die out, peeling develops. The appointment of therapy is possible only after establishing the exact diagnosis. The choice of drugs for this type of athlete's foot with blisters is made on an individual basis. Systemic and local drugs are most often shown.
Onychomycosis
This disease is a type of fungus of the foot that is characterized by a fungal infection of the nail. You can get infected in public showers, saunas, baths, swimming pools. Dandruff, which contains a pathogenic microorganism, is easily detached from the nail plate and can be left on floors, carpets, mats, and unpainted benches. High humidity not only allows them to survive, but also promotes active reproduction, which significantly increases the risk of infection.
In the initial stages, the infection penetrates the epidermis of the feet and causes severe itching. To lessen the unpleasant sensations, the person begins to comb the infected area, but this only makes the situation worse. Areas of the skin affected by the fungus are covered with small scratches and cracks, microorganisms begin to spread, penetrate under the nail plate and then begin to multiply in an uncontrolled manner.
Serious illnesses such as diabetes or HIV, circulatory disorders and nail trauma greatly increase the risk of infection.
Onychomycosis is divided into 3 types:
- Normotrop. With this type of onychomycosis, a change in nail color from normal to yellow-brown is observed. Natural shine, nail shape and thickness remain unchanged.
- Hypertrophic. The color of the nail changes definitively, its shine disappears, the shape changes, a thickening develops and partial destruction begins.
- Onycholytic. The affected nail turns brown in color, thins and begins to break. His gradual separation from the bed begins. Uneven layers can be observed in the open part of the nail bed.
Therapy of this type of fungus on the palms of the hands and feet with topical medication is ineffective because the spores of the fungus are located under the nail. Before starting treatment, the nail should be removed. This is done with keratolytic drugs, and patches are also used. In some cases, there is the option of mechanical removal of the nail: the dead particles of the nail are cut off with a nail file or nail nippers. It is important to remember that all instruments used must be sterile.
The combined use of mechanical removal and keratolytic patches is the most effective way to remove a diseased nail. From keratolytic agents, you can use a ready-made set, which includes a special ointment, files for scraping the nail and a plaster. After the nail plate is removed, you should start taking systemic antifungal drugs.
It is quite difficult to determine the type of athlete's foot from the photo.

Interdigital (intertriginous) form
The most common and unpleasant form of the pathology is the intertriginous form of fungal infection. Appears quite often in summer, begins to develop between the third and fourth toes. Over time, the lesion spreads to areas between the other fingers.
At the very beginning, a small crack, funnel, or wound appears in the fold that is between the fingers. It is surrounded by diaper rash or flaky skin that is slightly green in color. Most often the damage gets wet, sometimes pus appears. The extinguished type of mushroom is characterized by a pronounced or flour-like peeling, as if there is flour on the surface of the finger. A similar impression is created by the large number of affected scales that detach from the skin. There is a slight itchiness that does not cause severe discomfort.
In an advanced form of the disease, there is delamination of the nails, severe coarsening, multiple cracks, horn-like compaction-like corns, pronounced yellowing.
In very rare cases, weeping disease develops - an exudative fungus. The main difference is that vesicles are poured out on the affected areas - bubbles filled with liquid. Therapy should be carried out comprehensively. Antifungal drugs are used as topical agents. In the more advanced form of the disease, systemic antifungal drugs are used. Treatment should continue until the fungus is completely gone.
Squamous-cell hyperkeratotic form
This type of athlete's foot (pictured below) is not very common.
Psoriasis is the process of pathogenic fungi penetrating the outer skin cells. Hyperkeratosis is the formation of the stratum corneum, which leads to a thickening of the dermis. In this regard, the squamous-epithelial-hyperkeratotic form of mycosis has several other names, for example "moccasin fungus" and "athlete's foot".
Squamous cell hyperkeratotic mycosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The sole of the foot is covered with a thickened keratinized layer of the dermis, which creates the impression that moccasins are worn on the foot.
- The coarsening of the sole occurs so much that it is covered with wide and rather thick calluses.
- Painful cracks appear on the corns.
- The peeling takes on a slimy type, a pattern on the skin is visible to the naked eye.
- Unbearable itching occurs.
- Over time, the nails begin to thin, break, and crumble.
When treating moccasins, it is very important first of all to remove the stratum corneum of the skin. This is done with soap and soda foot baths, compresses, salicylic compresses and ichthyol ointments. Salicylic ointment is used in dosages up to 10%. Creams based on petroleum jelly, ointments with lactic acid are effective. If you can't do this at home, you should seek help from a podiatry center. With the help of a hardware manicure, the specialist carefully removes the keratinized dermis.
Further treatment for the type of athlete's foot depends on the type of pathogen. It should only be started after an accurate diagnosis. It is not recommended to treat moccasin mycosis without first removing the stratum corneum of the skin - the active ingredients in the composition of the drug can not penetrate and reach the focus of infection. As a result, all efforts will be ruined.
Photos of types of athlete's foot cannot reflect all of the uncomfortable symptoms a person is experiencing.
hydrated form
Vesicular fungus, or, as it is also known, dyshidratic mycosis, is the rarest form of the disease. Its main manifestation is numerous vesicles that are grouped into conglomerates. Vesicles are vesicles that are filled with pus or nutrient fluid from the inside. When the fluid starts to become cloudy, the vesicles burst, ulcers remain in their place. They begin to merge into a line and form pronounced scars on the skin. This is due to the drying out and peeling of the layers of the skin.
About 70% of vesicular fungus infections are accompanied by allergic rashes. A variety of bacteria and viruses begin to invade the ulcer. This mixes up the disease and makes it more difficult to identify the causative agent. Therefore, you should immediately consult a doctor as soon as the primary symptoms appear (picture): He can quickly identify the type of athlete's foot and start therapy.
And that should be done immediately. Before using antifungal drugs, the acute process should first be eliminated. It is better to entrust this task to a specialist: he can gently pierce the vesicles, treat the remaining ulcers with 2% boric acid and smear them with brilliant green solution or methylene blue.
Treatment of the disease in its neglected form involves the use of corticosteroid ointments. After eliminating the inflammatory process, it is recommended to use local antifungal drugs. This suppresses the causative agent of the disease.
We keep looking at the names and types of athlete's foot.
Deleted form
Mycosis of the deleted form is almost invisible, its symptoms are minimal. These include: slight itching, burning, peeling of the type of mucus, microcracks in the interdigital zones. If you do not consult a specialist at the first signs of the disease, the pathology can pass into the form of onychomycosis, which is much more difficult to treat. In this case, the detached nail grows back from one month to six.
Treat the mycosis of the cleared form with local preparations: ointments, creams, foams. They allow you to form a layer on the foot that protects against other infections. It is not recommended to wash your feet within 24 hours of using such a medicine.
Systemic therapy can only be prescribed in extreme cases. The problem is that such drugs are toxic and negatively affect some internal organs, for example, the liver. Therefore, if the use of local remedies is having an effect, it is better not to take pills.
Treating athlete's foot with alternative methods
The photos of pathology presented in large numbers in the article do not cancel a trip to the doctor.
It is now very easy to choose a drug. However, many people prefer to treat the fungus with folk remedies. We offer several proven recipes:
- Cleaning the feet. The legs are warmed up in a basin with hot water, rubbed generously with laundry soap and treated with a stiff foot brush for five minutes. The foam is rinsed off. Actions are repeated 4-5 times. Then the feet are wiped dry and coated with cream.
- Celandine baths. 50 g of herbs are poured with 1. 5 liters of boiling water, heated on fire for 4-5 minutes and cooled. The feet should be kept in a warm broth for 30 minutes. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
- Tea tree oil is a powerful antiseptic. It must be rubbed repeatedly into the affected areas.
- You can get rid of itching and cracks with sour cream. She lubricates her legs before going to bed. The duration of therapy is 1 week.
- Baking powder. Eliminates burning and itching of the skin. The powder is mixed with water to make a thick mass. It is applied to the affected areas, wait for it to dry, then rinse off.
- Marigold. Flowers (50 gr. ) Are poured with boiling water (1: 2), insisted for 30 minutes, filtered. Infusion of smeared feet at night.

prevention
The simplest preventive measures will greatly reduce the likelihood of infection. Only personal items may be used, nails should be treated with sterile instruments. When visiting public places such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, beaches, you should wear your own shoes. By the way, try to choose it so that it is comfortable and your legs can breathe.
You should think about prevention in advance so that you don't have to deal with different types of athlete's foot later. The photo is far from showing all the options for the development of the disease.